Click here to sign in with or
Forget Password?
Learn more
share this!
15
7
Share
Email
May 17, 2022
by National Research Council of Science & Technology
In South Korea, which relies on imports for 99.3% of its metal resources, the per capita consumption of those metal resources is the highest in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, and consumption of precious metals in industries such as renewable energy, healthcare and semiconductors is increasing. Gold is in demand for applications such as batteries, electric vehicles and renewable energy in the electric and electronic industries, but is a big variable in the industry due to its limited availability and high cost. Thus, research on urban mining, which extracts precious metals from waste, is being actively conducted around the world. However, most of the technologies for extracting high-purity gold from waste resources require large amounts of chemicals and high operating temperatures; therefore, it has regulatory and efficiency problems.
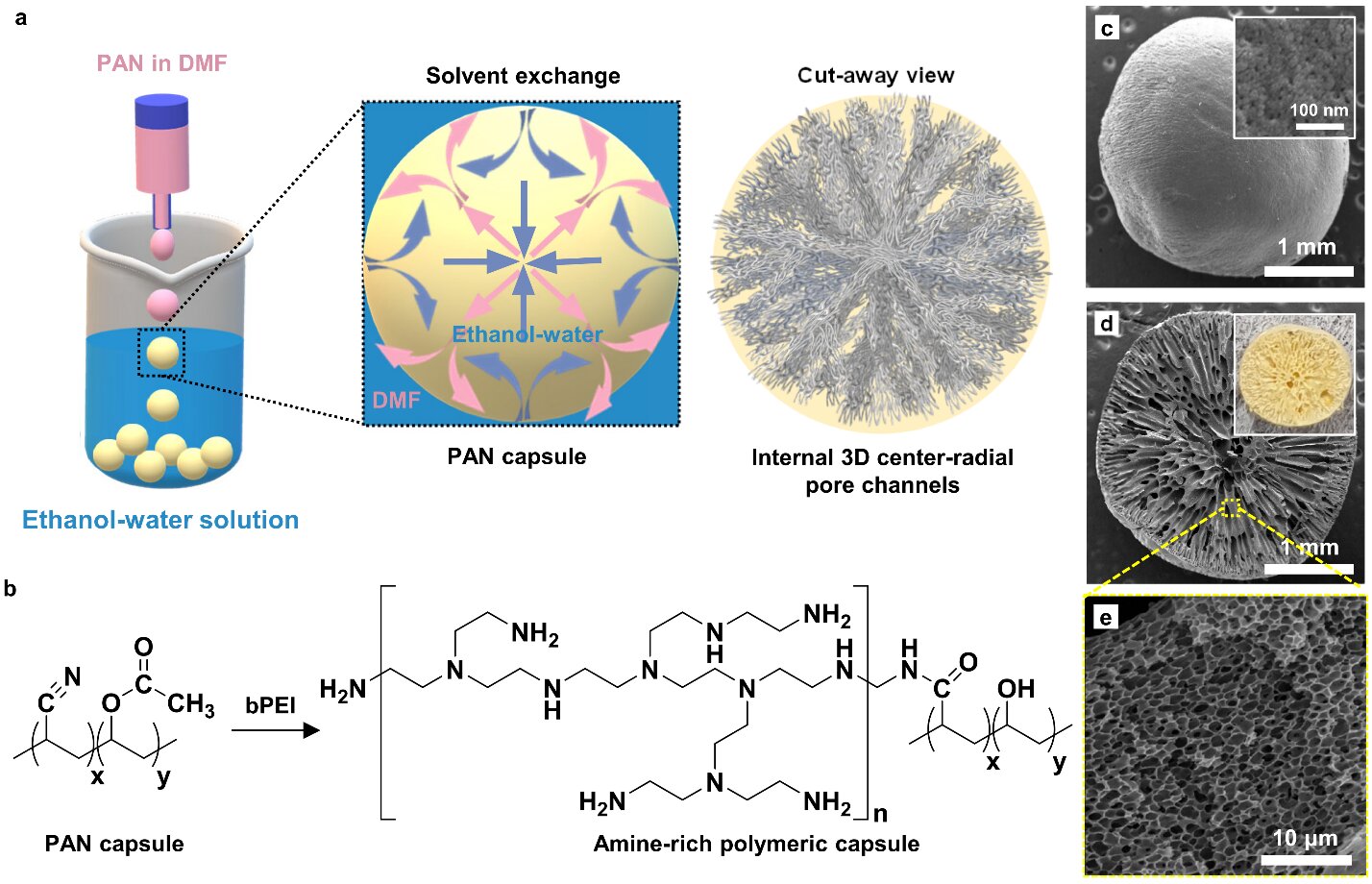
A Korean research team has developed a technology that can dramatically increase the recovery rate of precious metals from waste. The research team, comprising Dr. Jae Woo Choi and Dr. Kyung-Won Jung from the Center for Water Cycle Research at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), reported that they developed a gold recovery process with the world’s highest recovery efficiency of 99.9 %. The technology is a capsule-type material in which a polymeric shell surrounds a multi-layered internal structure.
The developed material has the advantage of high recovery efficiency compared to conventional adsorption materials since the material traps gold ions inside the capsule for recovery. The material also has the advantage of preventing the clogging of the internal porous structure since the polymeric shell allows gold ions to penetrate while being impermeable to suspended solids present with gold. By introducing functional groups that react only with gold ions in the multi-layered internal structure, gold that has passed through the polymeric shell could be stably recovered even with the coexistence of 14 types of ions and 3 types of suspended solids. Capsule-type material can be produced through a continuous process based on the solvent exchange method, and its efficiency and stability were demonstrated by maintaining a recovery performance of 99.9% or more even when the material was reused 10 times.
The authors write, “The material developed through this research solves the problems of conventional materials developed for the recovery of precious metals. Moreover, it can be immediately applied to related industrial processes as they can be easily synthesized in large quantities. Through this study, it was evident that the chemical properties and morphology of the recovered material could also play a very important role in recovering metal resources from the water.”
The lead author, Dr. Youngkyun Jung of KIST, said, “The results of this research are expected to serve as a basis for the development of the first eco-friendly process in Korea that can selectively recover and refine metal resources from waste and precious metal scraps generated in various industries, such as automobiles and petrochemicals.”
The results of the research were published in the latest issue of the Chemical Engineering Journal.
Explore further
Facebook
Twitter
Email
Feedback to editors
12 hours ago
0
14 hours ago
0
14 hours ago
0
14 hours ago
0
May 16, 2022
1
6 hours ago
6 hours ago
6 hours ago
6 hours ago
6 hours ago
6 hours ago
6 hours ago
40 minutes ago
45 minutes ago
54 minutes ago
1 hour ago
1 hour ago
1 hour ago
More from Physics Forums | Science Articles, Homework Help, Discussion
May 13, 2022
Apr 24, 2020
Apr 08, 2022
Mar 22, 2022
Apr 15, 2022
Aug 26, 2016
8 hours ago
15 hours ago
May 16, 2022
May 16, 2022
May 16, 2022
May 16, 2022
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form. For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient’s address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we’ll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Medical research advances and health news
The latest engineering, electronics and technology advances
The most comprehensive sci-tech news coverage on the web
This site uses cookies to assist with navigation, analyse your use of our services, collect data for ads personalisation and provide content from third parties. By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
Author Profile
Latest entries
 राशीफल2024.04.25Aaj Ka Rashifal: कर्क और कन्या राशि वालों को कार्यक्षेत्र में मिल सकती है तरक्की, पढ़ें दैनिक राशिफल – अमर उजाला
राशीफल2024.04.25Aaj Ka Rashifal: कर्क और कन्या राशि वालों को कार्यक्षेत्र में मिल सकती है तरक्की, पढ़ें दैनिक राशिफल – अमर उजाला लाइफस्टाइल2024.04.25Winter & Migraine: इस मौसम में ट्रिगर हो सकती है माइग्रेन की समस्या, जानिए इसके कारण और बचाव के उपाय – अमर उजाला
लाइफस्टाइल2024.04.25Winter & Migraine: इस मौसम में ट्रिगर हो सकती है माइग्रेन की समस्या, जानिए इसके कारण और बचाव के उपाय – अमर उजाला धर्म2024.04.25'राजनीति का धर्म ' या 'धर्म की राजनीति' | Relation Between Politics and Religion – Hindi Oneindia – Oneindia Hindi
धर्म2024.04.25'राजनीति का धर्म ' या 'धर्म की राजनीति' | Relation Between Politics and Religion – Hindi Oneindia – Oneindia Hindi टेक2024.04.2522 New Technology Trends for 2024: New Tech Horizons – Simplilearn
टेक2024.04.2522 New Technology Trends for 2024: New Tech Horizons – Simplilearn